If you’ve ever stepped into a laboratory, chances are you’ve encountered a rotary evaporator. This essential piece of equipment is a staple for chemists, researchers, and technicians alike. But what exactly does it do, and why is it so vital? Let’s explore its functions and why it remains an indispensable tool in modern laboratories.
Basic Working Principle of a Rotary Evaporator
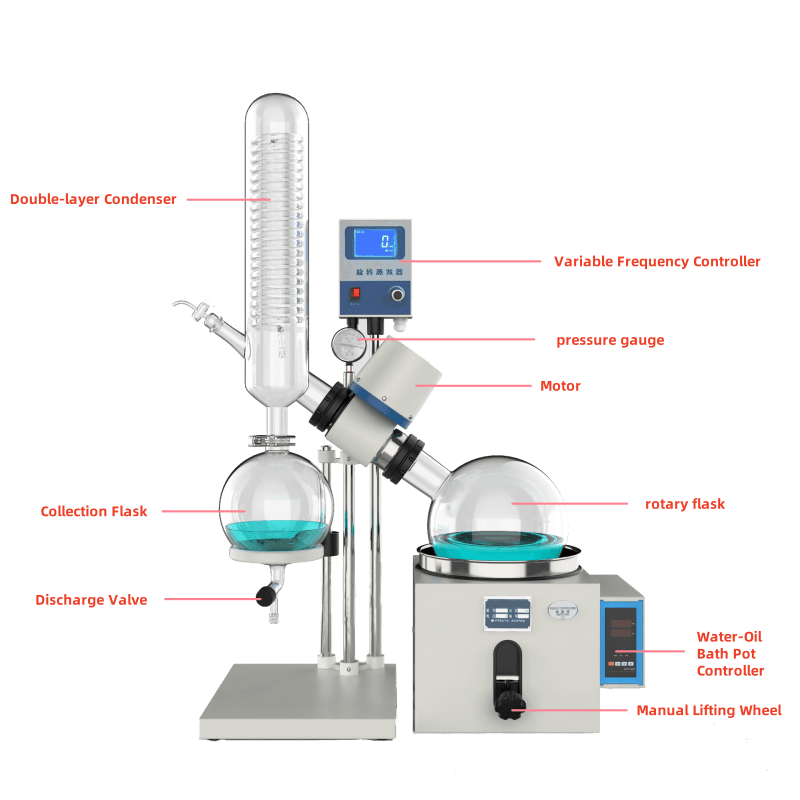
At its core, a rotary evaporator works by using vacuum pressure, gentle heat, and rotation to evaporate solvents from samples. The system consists of:
- A rotating flask where the liquid sample is placed.
- A water or oil bath for controlled heating.
- A condenser to cool and collect evaporated solvents.
- A vacuum pump to lower the boiling point of solvents.
By reducing the pressure, the boiling point of the solvent decreases, allowing it to evaporate at much lower temperatures. This prevents thermal degradation of sensitive compounds.
Core Functions of a Rotary Evaporator
Solvent Removal
One of the primary uses of a rotary evaporator is to remove solvents from mixtures. This is critical in organic synthesis, where solvents must be eliminated to isolate pure compounds. Additionally, the collected solvent can often be reused, saving resources.
Concentration of Solutions
Need to reduce the volume of a solution? Rotary evaporators are excellent for concentrating samples. For example, in biological research, evaporators are used to concentrate DNA or protein solutions before analysis.
Crystallization Processes
In industries like pharmaceuticals, rotary evaporators play a crucial role in crystallization. By carefully controlling the evaporation process, scientists can promote the formation of high-purity crystals.
Advantages of Using a Rotary Evaporator
Time-Saving Benefits
Compared to traditional evaporation methods, rotary evaporators are significantly faster. Their ability to handle multiple samples simultaneously makes them a time-efficient choice for laboratories.
Enhanced Safety Measures
With enclosed systems, rotary evaporators minimize the risk of exposure to harmful chemicals. They also allow for precise temperature and pressure control, ensuring safe operation.
Industries and Applications
Pharmaceutical Laboratories
Rotary evaporators are indispensable in drug development, helping isolate active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and refine formulations.
Food and Beverage Industries
Ever wondered how natural flavors are extracted for your favorite foods? Rotary evaporators help concentrate flavors and remove unwanted solvents, ensuring the end product is pure and safe.
Environmental Research
From analyzing pollutants to extracting environmental contaminants, rotary evaporators support eco-friendly research by enabling precise sample preparation.
How to Optimize Rotary Evaporator Usage
Choosing Optimal Parameters
Maintaining the right temperature and rotation speed is crucial. A balance ensures efficient solvent evaporation without overheating your sample.
Regular Maintenance Practices
Cleaning the glassware, checking vacuum seals, and storing the equipment properly can extend its lifespan and maintain its efficiency.
Common Challenges and Solutions
- Overheating: Avoid by monitoring bath temperature closely.
- Incomplete Solvent Recovery: Ensure the vacuum pump and condenser are functioning correctly.
Innovations in Rotary Evaporators
Modern rotary evaporators come with digital displays, automated controls, and energy-saving designs, making them more efficient and user-friendly than ever.
In summary, the rotary evaporator is an essential tool for any laboratory, enabling solvent removal, concentration, and crystallization with unmatched precision and safety. Its versatility makes it a cornerstone in fields ranging from chemistry to food science.
FAQs
- What is a rotary evaporator used for?
It’s used to remove solvents, concentrate solutions, and assist in crystallization processes. - Can rotary evaporators handle high-boiling-point solvents?
Yes, but proper temperature control and vacuum adjustments are essential. - What is the ideal vacuum pressure for efficient operation?
It depends on the solvent, but typically ranges from 50 to 100 mbar. - How do you clean a rotary evaporator?
Disassemble the glassware, rinse with appropriate solvents, and dry thoroughly before reassembly. - Are rotary evaporators suitable for beginners?
Absolutely! Modern models are user-friendly and come with clear instructions for safe operation.



