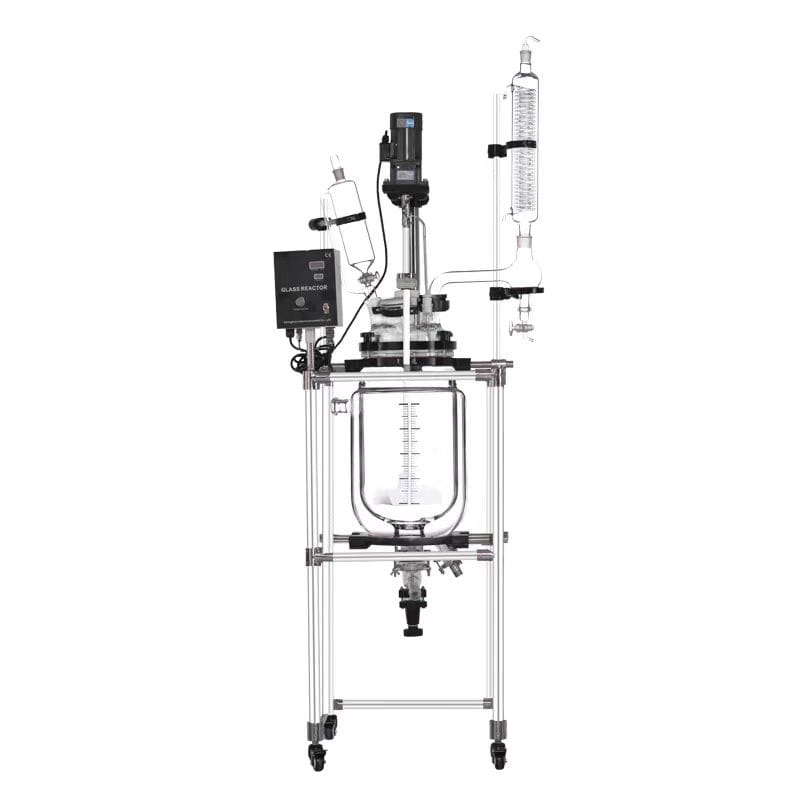
1. Introduction: What are Glass Reactors?
Glass reactors, both single-layer and double-layer, are indispensable tools in modern laboratories and chemical industries. These reactors are known for their transparency, excellent corrosion resistance, and the ability to operate under various temperature and pressure conditions. Whether for synthetic chemistry, pharmaceutical development, or bioengineering, glass reactors play a crucial role in achieving safe, controlled, and efficient reactions. This article will explore the differences between single-layer and double-layer glass reactors, their advantages, and key applications.
2. Single Glass Reactors: Simplicity and Versatility
Definition and Features
A single glass reactor is designed with one layer of glass, making it ideal for simple reactions that do not require complex temperature control. These reactors allow clear visibility of the reaction process, which helps researchers monitor the progress in real-time.
- Material: Borosilicate glass is commonly used for its thermal stability and chemical resistance.
- Operating Conditions: Suitable for reactions at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures, as well as in low-pressure environments.
Applications
Single glass reactors are used in various fields such as organic chemistry, material synthesis, and educational labs. They are perfect for tasks like crystallization, mixing, and mild thermal reactions.
Advantages
- Cost-effective: Single glass reactors are relatively affordable and easy to maintain.
- Simplicity: Ideal for basic reactions without the need for intricate temperature controls.
- Transparency: Complete visibility of the reaction process.
3. Double Glass Reactors: Precision and Control
Definition and Features
Double glass reactors consist of two layers of glass, with a space between them that can be filled with heating or cooling fluids. This design allows for precise temperature control, making these reactors suitable for reactions requiring extreme heating or cooling.
- Material: Like single reactors, these are also made from borosilicate glass, which can handle a wide range of chemicals and temperatures.
- Temperature Range: Capable of managing temperatures as low as -80°C and as high as 300°C.
- Heating/Cooling: The external jacket allows for the circulation of thermal fluids, providing precise control of the reaction environment.
Applications
Double glass reactors are ideal for more complex reactions, especially those that require specific thermal environments, such as polymerization, distillation, and solvent extraction. They are frequently used in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries where reaction stability is paramount.
Advantages
- Precise Temperature Control: The ability to control the reaction temperature accurately is crucial for many industrial and laboratory applications.
- Safety: The double-layer design helps in maintaining stable temperatures, reducing the risk of thermal runaway.
- Versatility: Can handle both heating and cooling requirements efficiently.
4. Key Differences Between Single and Double Glass Reactors
Understanding the differences between these two types of reactors is essential for selecting the right equipment for your specific needs.
| Feature | Single Glass Reactor | Double Glass Reactor |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Minimal control | Precise control with a jacket |
| Applications | Simple reactions | Complex, temperature-sensitive reactions |
| Cost | More affordable | Higher cost due to additional features |
| Suitability | Ideal for basic lab processes | Best for industrial and pharmaceutical use |
| Visibility | Full visibility of the reaction | Same level of transparency |
5. Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Needs
When deciding between a single or double glass reactor, consider the following factors:
- Nature of the Reaction: If your reaction requires precise temperature control, a double glass reactor is essential. For simpler reactions, a single glass reactor may suffice.
- Budget: If budget constraints are significant, a single glass reactor is a cost-effective solution.
- Scalability: For large-scale industrial processes, double glass reactors offer the flexibility and control necessary for safe and efficient production.
6. Conclusion
Both single and double glass reactors serve critical roles in various chemical processes, offering unique advantages depending on the specific application. For simple, room-temperature reactions, single glass reactors provide an affordable and reliable option. In contrast, double glass reactors are the go-to choice for reactions that demand precise temperature control and a high degree of safety.
If you are in the market for glass reactors, understanding the specific requirements of your application will guide you in selecting the appropriate reactor. For expert advice or to explore our range of glass reactors, feel free to contact us.