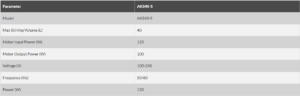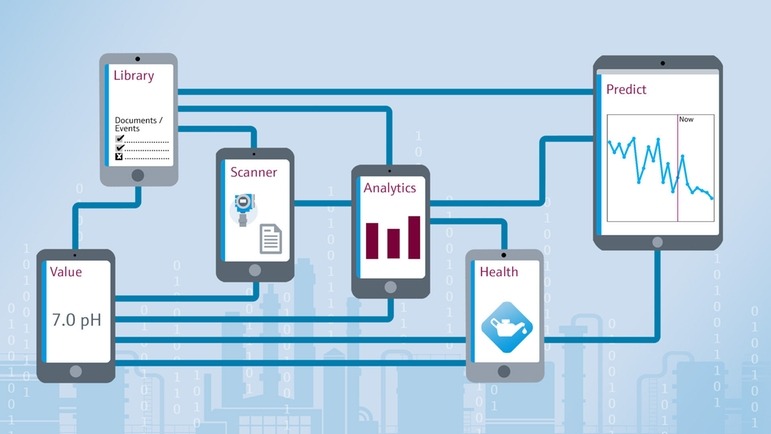
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing industries by connecting devices, enabling real-time data exchange, and automating processes. In the chemical instrument sector, IoT is driving innovation and improving operational efficiency in laboratories and industrial settings. This article explores the impact of IoT on chemical instruments and its benefits for laboratories and manufacturers.
1. Real-Time Monitoring and Data Collection
IoT-enabled chemical instruments allow for real-time monitoring of various parameters, such as temperature, pressure, and chemical composition. These instruments can transmit data continuously to cloud-based platforms, providing scientists and engineers with immediate access to critical information. This capability enhances the accuracy of experiments and production processes, ensuring that deviations are detected and addressed promptly.
For instance, in pharmaceutical production, real-time monitoring of reaction conditions can help optimize yields, improve product quality, and reduce the risk of costly errors.
2. Remote Access and Control
One of the most significant advantages of IoT in chemical instruments is the ability to remotely control equipment. Researchers and technicians can monitor and adjust instrument settings from any location, reducing the need for on-site personnel. This feature is especially useful in large-scale industrial settings or when managing multiple laboratories.
Remote control of instruments not only improves efficiency but also minimizes downtime by allowing users to troubleshoot issues and perform maintenance without being physically present. This results in faster response times and reduced operational costs.
3. Predictive Maintenance
IoT technology enables predictive maintenance by continuously monitoring the performance of chemical instruments. By analyzing data collected over time, IoT systems can identify signs of wear, malfunction, or inefficiency before they result in equipment failure. This proactive approach helps prevent unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of instruments.
Predictive maintenance is particularly valuable for expensive, high-precision chemical instruments, where unexpected breakdowns can lead to significant financial losses and delays in research or production.
4. Enhanced Data Integration and Analytics
IoT facilitates seamless integration between chemical instruments and laboratory information management systems (LIMS) or enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. This integration enables the automatic transfer of experimental data, making it easier for laboratories to manage data, conduct analysis, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Advanced analytics powered by IoT can also uncover insights into equipment performance, experiment outcomes, and resource utilization. Laboratories can use these insights to optimize processes, improve decision-making, and ensure the repeatability of experiments.
5. Improved Sustainability
By optimizing chemical processes and reducing waste, IoT-enabled instruments contribute to more sustainable laboratory practices. Real-time data allows researchers to fine-tune experimental conditions, minimizing the use of energy and resources. Additionally, IoT systems can monitor the environmental impact of processes, such as emissions and waste production, helping laboratories reduce their carbon footprint.
As sustainability becomes a priority for many industries, IoT technology offers a path to greener chemical research and production methods.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT technology into chemical instruments is transforming the way laboratories and industrial facilities operate. From real-time monitoring and remote control to predictive maintenance and enhanced data integration, IoT-enabled instruments provide numerous benefits that improve efficiency, reduce costs, and contribute to sustainability. As the chemical instrument industry continues to evolve, IoT will play a critical role in shaping the future of research and production processes.