Rotary evaporators, commonly referred to as “rotavaps,” are indispensable tools in laboratories worldwide. They enable the efficient removal of solvents from mixtures through evaporation under reduced pressure. In this article, we delve deeply into the principles of rotary evaporators, their components, functionality, and applications, offering a comprehensive guide for researchers and industry professionals alike.
What is a Rotary Evaporator?
A rotary evaporator is a laboratory device designed to gently remove solvents from samples via a combination of heat, vacuum pressure, and rotational motion. It is extensively used in chemical synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and food industries to recover and concentrate substances.
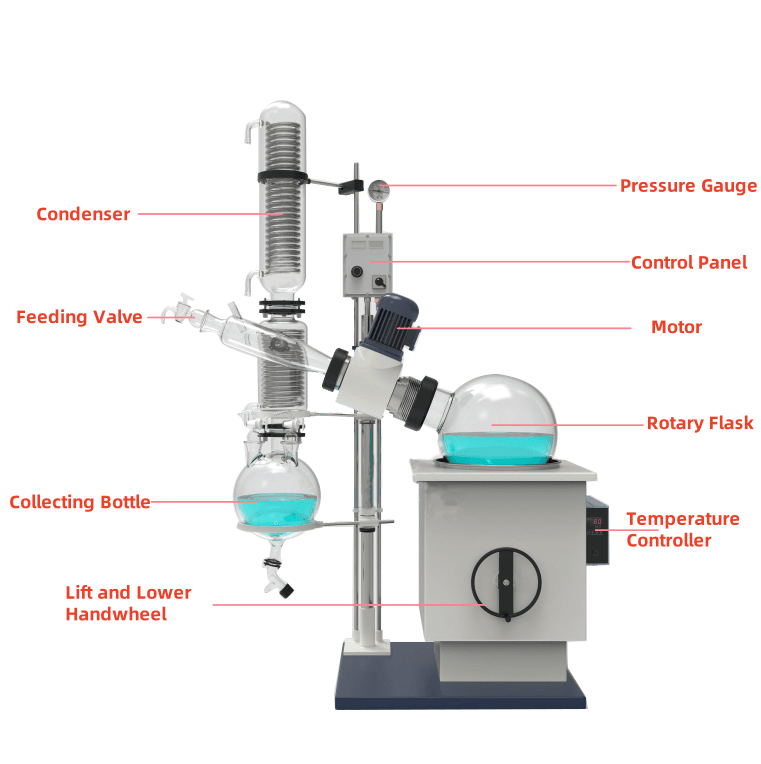
Key Components of a Rotary Evaporator
- Rotating Flask: The container where the liquid mixture is placed. The flask rotates continuously to increase the surface area for evaporation.
- Water or Oil Bath: Provides controlled heating to facilitate solvent evaporation.
- Condenser: Equipped with cooling coils to condense the evaporated solvent back into a liquid for collection.
- Vacuum System: Reduces the pressure within the apparatus, lowering the boiling point of solvents.
- Receiving Flask: Collects the condensed solvent for reuse or disposal.
- Control Panel: Enables precise adjustment of rotation speed, temperature, and vacuum pressure.
The Principle of Rotary Evaporation
At its core, the rotary evaporator operates on the principle of evaporation under reduced pressure. By decreasing the pressure in the system, the boiling point of the solvent is significantly lowered, allowing for gentle and efficient solvent removal without decomposing heat-sensitive substances.
The process can be summarized in these key steps:
- Sample Preparation: The mixture is placed in the rotating flask.
- Heating: The water or oil bath provides uniform heat to the flask, encouraging solvent molecules to transition into the vapor phase.
- Rotation: The flask’s rotation creates a thin film of liquid, increasing the surface area and enhancing evaporation efficiency.
- Vacuum Application: The vacuum system reduces the pressure, lowering the solvent’s boiling point and enabling evaporation at lower temperatures.
- Condensation: The vaporized solvent passes through the condenser, where it is cooled and converted back to liquid.
- Collection: The liquid solvent is collected in the receiving flask for subsequent use or disposal.
Advantages of Using Rotary Evaporators
Rotary evaporators offer several advantages that make them indispensable in scientific and industrial applications:
- Efficient Solvent Recovery: Reduces waste and costs by reclaiming solvents for reuse.
- Protection of Heat-Sensitive Compounds: The low-temperature process prevents the degradation of volatile or thermolabile substances.
- Time-Saving: Enhanced evaporation speed compared to traditional methods.
- Scalability: Available in various sizes to accommodate small-scale laboratory needs or large industrial processes.
Applications of Rotary Evaporators
Chemical Synthesis and Purification
Rotary evaporators are vital in chemical laboratories for removing solvents after synthesis, purifying reaction products, and concentrating solutions.
Pharmaceutical Industry
They are widely used in drug formulation processes, including extracting active ingredients and concentrating compounds for clinical research.
Food and Beverage Industry
Rotary evaporators play a crucial role in flavor extraction, concentration of natural products, and the development of new food formulations.
Environmental Analysis
In environmental laboratories, rotary evaporators assist in analyzing pollutants by concentrating trace chemicals from large-volume samples.
Factors Affecting Evaporation Efficiency
- Boiling Point of Solvent: Solvents with lower boiling points evaporate faster under vacuum conditions.
- Vacuum Pressure: Proper adjustment ensures efficient evaporation without bumping or foaming.
- Rotation Speed: Optimizing speed enhances the formation of a thin liquid film, accelerating evaporation.
- Temperature: Precise control of the bath temperature prevents thermal degradation of sensitive compounds.
- Condenser Cooling: Effective cooling ensures rapid condensation of the vapor.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance of a rotary evaporator ensures optimal performance and longevity. Key practices include:
- Cleaning Components: Periodically clean the rotating flask, condenser, and receiving flask to prevent contamination.
- Inspecting Seals and Gaskets: Check for wear or leaks that may compromise vacuum efficiency.
- Monitoring Vacuum Levels: Ensure the vacuum pump functions correctly for consistent pressure.
- Lubricating Moving Parts: Reduce wear and tear on rotating mechanisms.
If operational issues arise, such as reduced evaporation rates or solvent bumping, consider the following troubleshooting tips:
- Check Vacuum Integrity: Inspect for leaks in seals or connections.
- Adjust Rotation Speed: Too high or too low speeds can disrupt film formation.
- Optimize Bath Temperature: Ensure it aligns with the solvent’s boiling point under reduced pressure.
The rotary evaporator is an indispensable tool in modern laboratories, offering precise and efficient solvent removal for diverse applications. Understanding its principles and optimizing its operation ensures enhanced productivity and results in both research and industrial settings.